Country-wide CML rainfall
Two papers on country-wide rainfall estimation from CML data in Germany
Based on its real-time CML data acquisition system (Chwala et al., 2016) KIT has gathered a large data base with attenuation data from more than 4000 CMLs in Germany. Within IMAP the methods for processing this CML attenuation data to derive rainfall rates have been developed and implemented in the Python software package pycomlink. This methods have been applied and further refined in the first long-term analysis of CML rainfall information in Germany (Graf et al., 2020).
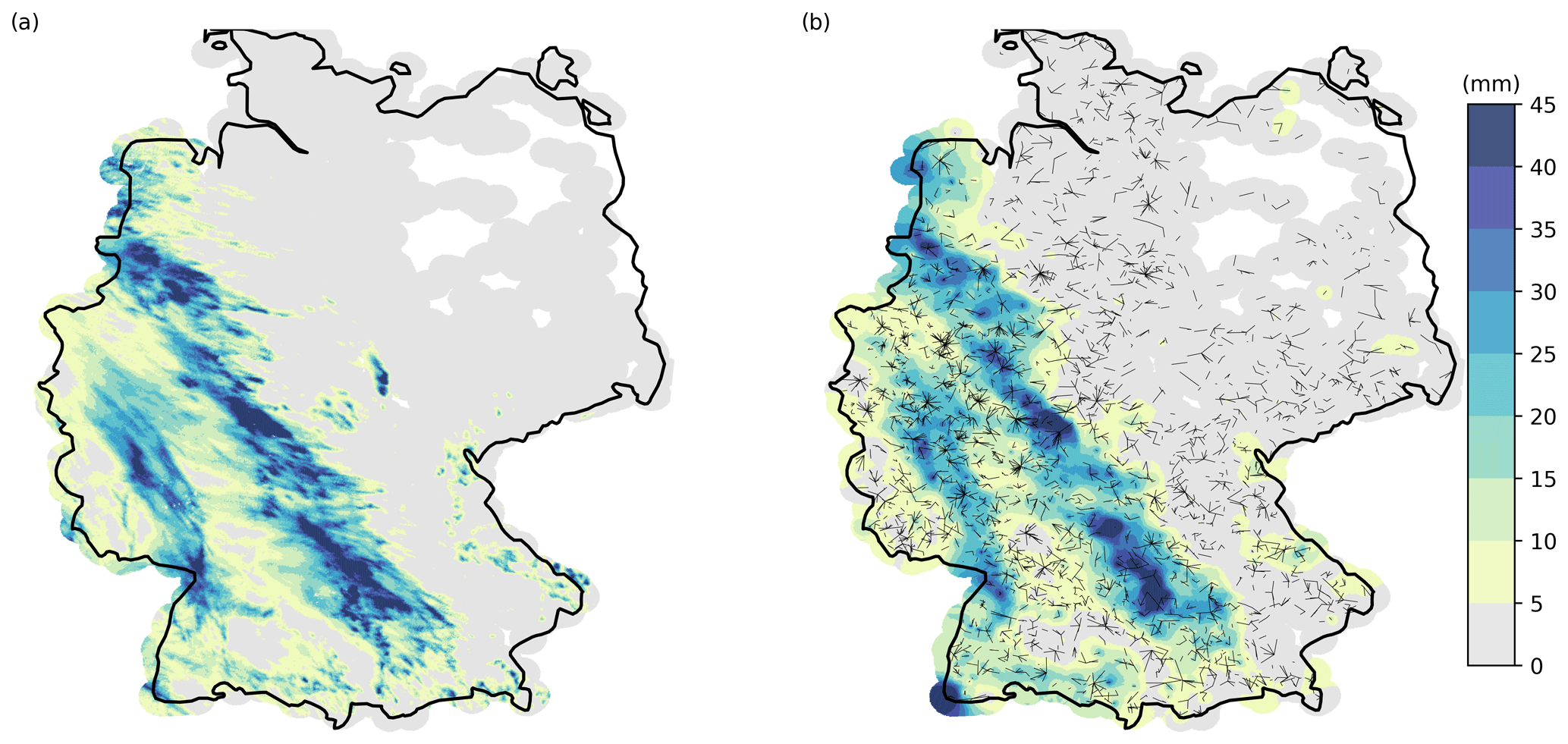 Accumulated rainfall for a 48 h showcase from 12 to 14 May 2018 for (a) RADOLAN-RW and (b) CML-derived rainfall. CML-derived rainfall is interpolated using a simple inverse distance weighting interpolation. A coverage mask of 30 km around CMLs is used. This showcase is visualized in a video supplement with an hourly resolution. (Source: Fig 7 in Graf et al., 2020)
Accumulated rainfall for a 48 h showcase from 12 to 14 May 2018 for (a) RADOLAN-RW and (b) CML-derived rainfall. CML-derived rainfall is interpolated using a simple inverse distance weighting interpolation. A coverage mask of 30 km around CMLs is used. This showcase is visualized in a video supplement with an hourly resolution. (Source: Fig 7 in Graf et al., 2020)
Comparison to the gauge-adjusted radar product RADOLAN-RW from the German Meteorological Service (DWD) showed good performance of the CML rainfall estimates during the warm season where liquid precipitation is prevalent. For the cold season, in particular for mountain regions, CML-derived rainfall sums showed considerable overestimation, which is most probably cause through wet snow or ice on the antennas.
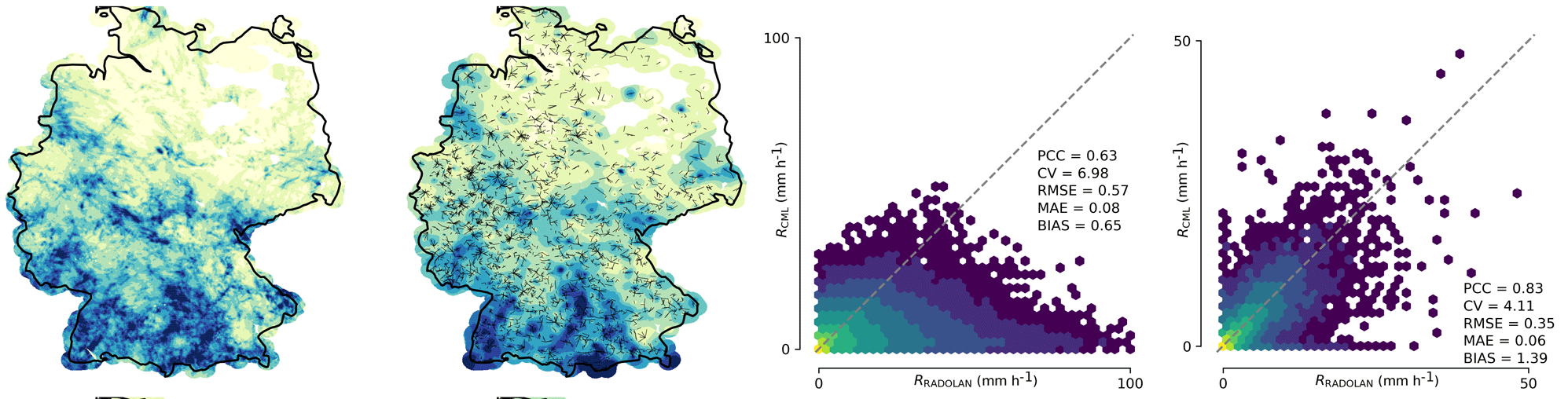 Monthly aggregations of hourly rainfall maps from CMLs compared to RADOLAN-RW for May 2018. Two scatter density plots are shown: one for pixel-by-pixel comparison of the hourly maps (map-based comparison), and one for the comparison of the hourly path-averaged rainfall along the individual CMLs (link-based comparison). (Source Fig 9 in Graf et al., 2020)
Monthly aggregations of hourly rainfall maps from CMLs compared to RADOLAN-RW for May 2018. Two scatter density plots are shown: one for pixel-by-pixel comparison of the hourly maps (map-based comparison), and one for the comparison of the hourly path-averaged rainfall along the individual CMLs (link-based comparison). (Source Fig 9 in Graf et al., 2020)
Because gauge-adjusted radar rainfall products are not perfect, a combination, and not only comparison,of RADOLAN and CML-rainfall is the logical next step. We are working on this topic in the new BMBF-funded research project HoWa-innovativ. In parallel we are continuing to improve CML data processing (Polz et al., 2020) and investigate how CML attenuation data can improve rainfall estimation from polarimetric weather radars within the DFG research group RealPEP.